Enterprise Operating Model for Enabling GenerativeAI
A step by step framework for ensuring successful GenerativeAI operating model in large organizations
Executive Summary
This article emphasizes the significance of structured integration of AI within organizations to drive innovation and efficiency. To successfully implement AI, companies must consider business value use cases, robust infrastructure, ethical policies, skilled resources, data accessibility, change management protocols, a sandbox for proof of concepts, an engineering philosophy based on hypotheses and experiments, security tailored for AI, and clear adoption strategies.
Leadership plays a crucial role, requiring a dedicated AI leader to orchestrate the integration across the business, supported by departmental leaders, external experts, and Centers of Excellence. This collaborative structure ensures the magnification of AI's impact, suggesting that AI should be a core facet of operational strategies, with proactive transformation directives to maintain a competitive edge.
The article highlights that AI's potential extends to transforming products, operations, and services, requiring organizations to integrate AI thoughtfully to remain at the forefront of innovation. Examples include Bank of America's AI-powered virtual assistant and Zafin's AI platform for optimizing financial products. AI also enhances security, finance, legal, and marketing functions, with vendors like Proofpoint, AppZen, Coupa, and DocuSign offering AI-powered solutions to address the complex challenges and opportunities presented by AI technology
In an era where artificial intelligence (AI) is redefining the boundaries of innovation and operational efficiency, the structures we establish within our organizations to shepherd AI investments and adoption are of paramount importance.
I see the integration of AI as a symphony, requiring a maestro and an orchestra working in harmony to create a masterpiece.
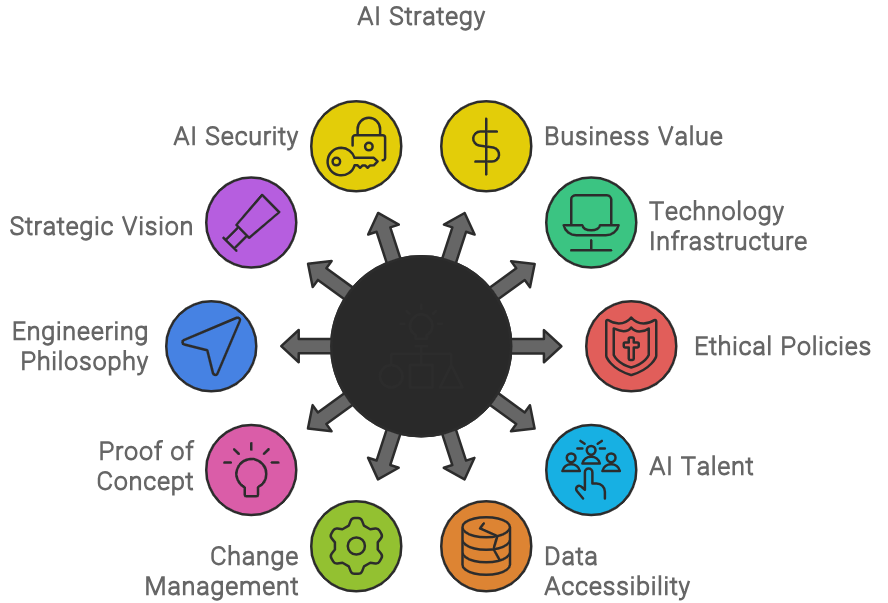
In order to ensure a successful future in AI at any organization, following aspects have to be considered and structure has to be in place.
Develop business value based use case
Infrastructure: Ensure proper technology infrastructure to support
Policies: Develop ethical or responsibility code and policies
Skills and resources: Hiring AI talent
AI-ready data sources by improving accessibility and/or hygiene. (accurate, enriched, fair, secure and governed)
Protocols: Build change management protocols
Sandbox environment to conduct proof of concept.
Hypothesis and experiment driven engineering philosophy.
AI-ready principles: Vision of AI with strategic business goals and values
AI-ready Security: the security risks for AI demand a new approach for protecting your company.
Adoption: Identify and prioritize where to deploy
Laying Foundations:
In order to ensure there is structure in place to drive the necessary transformation, a dedicated leader for AI is required. The dedicated AI leadership signifies the company's commitment to this transformative technology, ensuring that there's a clear vision and accountability. This role is pivotal, orchestrating the symphony of AI integration across various facets of the business.
Equally important are the departmental leaders who bring AI down to the functional level, ensuring its benefits are realized in every corner of the business, from marketing to manufacturing. They are the section leaders in our symphony, ensuring each instrument—each department—plays in tune with the larger AI strategy.
Collaborating with external experts, such as consulting firms or system integrators, allows us to imbibe external insights and best practices, much like inviting guest soloists to enhance the performance with their specialized expertise.
Lastly, the establishment of a structured working group or a Center of Excellence serves as the rehearsal space for innovation. It's where the continuous practice of integrating and refining AI applications takes place, ensuring that when the curtain rises, our business is ready to perform at its best.
Organizations need the right talent and infrastructure to leverage AI. For instance, hiring data scientists and investing in robust computing infrastructure are prerequisites for harnessing AI in financial forecasting and analysis.
The confluence of these structures creates a robust framework to not only manage but also magnify the impact of AI, thereby ensuring our company not only keeps pace with technological advancements but leads the charge in the AI revolution.
AI has potential to transform business, but we need to understand its implications.
In any organization, the advent of AI isn't merely a technological event—it's a pivotal chapter in our ongoing narrative of innovation and growth. I firmly believe that AI's implications ripple through every aspect of our business, necessitating a strategic and thoughtful approach to its adoption.
For our products and services, AI is not just a priority—it's a crucible for reinvention. It offers us the lens to re-evaluate our offerings, identify untapped opportunities, and gain deeper insights into our competitors. By actively involving AI in these discussions, we are not just future proofing our products but also crafting a roadmap that positions us at the vanguard of industry innovation.
On the operations front, AI is the linchpin for enhancement. Whether it's through streamlining processes, fortifying risk management, fostering collaboration, or steering future planning, AI stands as a beacon for operational excellence. We've transcended beyond considering AI; we need to integrate it as a core facet of our operational strategy, with a clear directive to transform these areas proactively.
I also recognize that the influence of AI is not restricted to a single facet but permeates through the IT, Security, and Finance functions of any organization. In IT, we should leverage AI for optimizing our cloud and infrastructure, ensuring the applications are both innovative and reliable.
As all organizations adopt AI, differentiation becomes challenging. However, unique AI applications in customer service or personalized banking can be a competitive advantage.
To harness AI's potential, Bank of America has invested in creating an AI-powered virtual assistant, Erica, which required significant resources but has since become a cornerstone of their digital strategy, engaging with millions of customers.
AI can help organizations launch new business products. Eg. many banks use AI to help model better products, address them to right customers.
Zafin is a vendor that uses AI for credit card modeling. Zafin's AI-powered platform helps financial institutions optimize their credit card offerings by analyzing customer data and providing insights into customer behavior, preferences, and intent. The platform also enables organizations to create personalized credit card offerings that match customer interactions and create integrated revenue streams to compete and grow.
Security is safeguarded through AI-enabled monitoring and robust zero-trust policies, vital in today's landscape of cyber threats.
Proofpoint uses generative AI techniques to develop advanced threat protection capabilities, such as email security and secure messaging. Their AI algorithms can analyze the content and context of emails and messages, identify potential threats, and take appropriate action to protect an organization's data and system
In Finance, AI can drive cost efficiency and informs our strategic spending, keeping us ahead of the curve in fiscal management. Embracing AI across these domains is not just strategic—it's imperative for our sustained leadership.
Vendors such as AppZen, Coupa, and SAP Concur offer AI-powered solutions that help organizations optimize their spend by automating expense auditing, detecting fraud, and identifying cost-saving opportunities. Also, AppZen's AI-powered platform uses machine learning to analyze expense reports and receipts, flagging any potential policy violations, errors, or fraud.
Legal teams are also pivotal in navigating the complex interplay between AI, liability, and data protection.
Vendors like DocuSign, LexisNexis leverage GenerativeAI to analyze the terms and conditions of a contract, identify potential risks and issues, and provide guidance on how to negotiate and finalize the agreement. This can lead to more favorable contract terms and a smoother negotiation process for businesses and individuals.
In marketing, AI can reshape customer engagement, customizing journeys, and refining pricing strategies with unparalleled precision. For shareholders, AI's predictive analytics offer sharper strategic alignment and risk assessment.
Adobe and Salesforce integrate to deliver AI-enabled customer engagement by leveraging their respective strengths. Adobe Experience Cloud provides a range of tools for creating personalized experiences, while Salesforce's Einstein provides AI-powered insights into customer behavior and preferences. By integrating these two platforms, organizations can create personalized experiences that are informed by AI-powered insights, resulting in higher engagement and better customer satisfaction.
In all these domains, AI is more than a technological tool—it's the embodiment of our commitment to progress and efficiency, ensuring that as we evolve, our business remains not only relevant but also resonant with the demands of a rapidly changing marketplace.
Enterprise Approach to Artificial Intelligence
I perceive the application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) as an essential strategic lever in today's corporate landscape. The approach a company adopts towards AI is reflective of its broader business ethos and innovation appetite.
A security-driven AI approach is commendably cautious but potentially myopic. By placing a singular emphasis on security, a company risks stifling the very innovation that AI can unlock. Conversely, an IT-driven stance, while technically astute, might neglect the integration of AI with core business objectives, leading to a misalignment that can impede both innovation and agility in line of business (LOB) operations.
The transformational strategy stands out as the North Star. This approach signifies a holistic alignment, weaving AI seamlessly across the company's fabric—from culture to customer value—thereby ensuring that AI initiatives resonate with the company’s strategic goals and intellectual property (IP) ethos.
However, 'Business as Usual' and 'Driven by a Vendor' paradigms indicate a passive or outsourced relationship with AI, respectively. These can lead to missed opportunities for internal growth or a dependency that might hinder a company's autonomous decision-making capabilities.
Lastly, the 'Independent or Siloed' approach, though innovative, lacks the structured integration with the company's vision, potentially creating a disjointed experience that may not fully realize the strategic benefits of AI.
A company’s AI strategy should be a balanced cocktail of security, innovation, and alignment with core business values, thereby propelling it towards a future where technology and human insight coalesce to drive transformational growth.
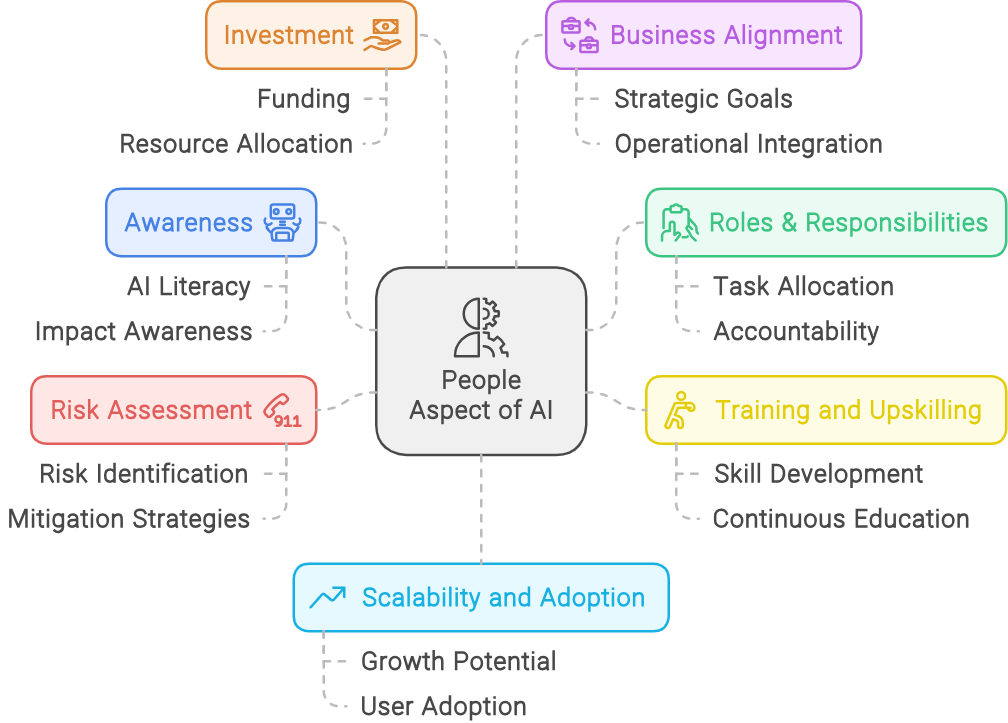
The People Aspect of AI in Enterprises
As an organization begins to enable AI transformation, developing a comprehensive view on what is needed when it comes to your people practices is determined by the following factors.
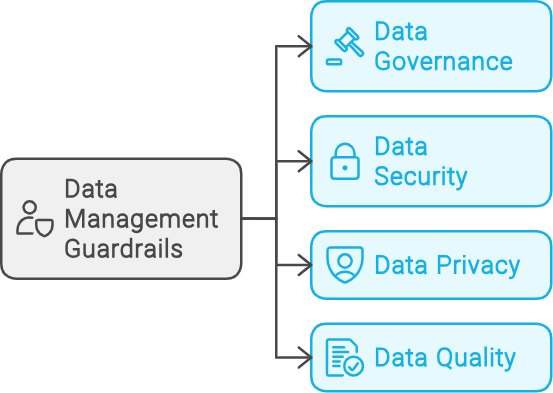
Guardrails required in organizations to support AI initiatives.
Data Management guardrails include the following components - data privacy and protection ensure sensitive information is secure. Access restriction controls who can view or use the data. Data quality focus on collecting accurate, relevant data. Data governance establishes policies for managing data responsibly, ensuring compliance, and maintaining ethical standards in AI development.
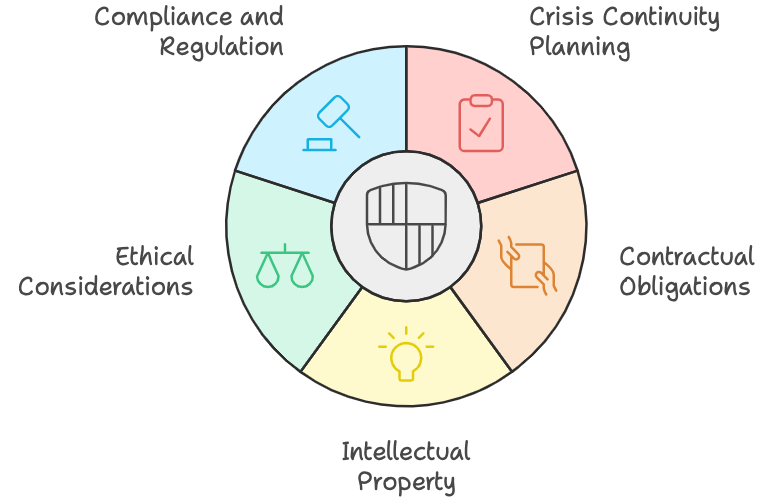
Changes in Technology Operations include business / crisis continuity planning prepares for disruptions to maintain operations. Contractual obligations ensure parties adhere to agreed terms. Intellectual property protects unique creations. Ethical considerations guide responsible AI use and development. Compliance and regulation require adherence to legal standards, promoting transparency, accountability, and fairness in AI practices.
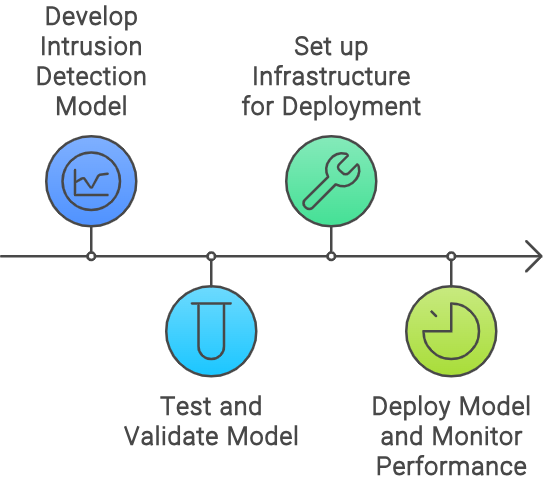
Technology and Architecture Practices include intrusion detection identifies and responds to security threats. Testing and validation ensure models are accurate and reliable. Infrastructure provides the hardware and software needed for operations. Model development and testing focus on creating and refining AI models. Deployment and monitoring involve implementing models and overseeing their performance in real-time.
Impediments around AI adoption
Having said that, there are lot of impediments that typically prohibit organization’s ability to reach AI goals. In the context of banking and financial services, these points reflect real and pressing concerns:
Data Privacy and Protection: Banks handle sensitive financial data. A breach can lead to a significant financial loss and damage to reputation. For example, implementing AI in fraud detection must ensure the confidentiality of customer data while identifying fraudulent transactions.
A real-life example includes the 2017 Equifax data breach, where sensitive information of millions of people was exposed. For banks adopting AI, the challenge is to strengthen cybersecurity measures to protect data while employing AI for enhanced security monitoring and fraud detection.
Risk vs. Reward: Financial institutions must balance the potential gains from AI investments against the risks. For instance, AI can optimize trading strategies, but if not properly managed, it could lead to systemic risks or significant financial losses.
In 2020, JPMorgan Chase's AI-powered trading system caused a sudden spike in stock prices, leading to a $100 million loss. The bank's AI system had been programmed to automatically execute trades based on market conditions, but it failed to account for a sudden change in market sentiment.
Legal Exposure: AI tools must comply with regulations like GDPR. Banks using AI for credit scoring must ensure that the algorithms do not inadvertently discriminate against certain groups, which could lead to legal repercussions.
Wells Fargo faced a lawsuit alleging that its algorithm discriminated against African American and Latino borrowers. Banks must ensure AI systems are transparent and unbiased to avoid such legal and reputational risks.
Accessibility of AI Tools: Banks need to democratize AI access so that employees across the bank can leverage insights for improved decision-making, like in risk assessment tools that can be used by loan officers without needing data science expertise.
Regulatory Compliance: Banks are heavily regulated, and AI systems used for regulatory reporting must be transparent and explainable to regulators to avoid penalties.
HSBC's use of AI in money laundering detection shows the importance of reliable AI systems that can consistently flag illegal activities without generating excessive false positives that can lead to operational inefficiencies.
Technical Debt: Rapid adoption of AI might lead to technical debt if legacy systems aren't updated or integrated properly. For example, integrating AI into outdated transaction systems can be challenging and costly.
In 2019, HSBC's voice recognition ID system was bypassed by a BBC reporter.
Reliability of AI: Consistency in AI predictions is critical, especially in risk modeling where inconsistent results could lead to inadequate capital reserves or improper risk assessments.
In 2020, Discover's AI-powered credit scoring model incorrectly classified a large number of customers as high-risk, leading to higher interest rates and fees. The company's AI system had been programmed to assess credit risk based on customer data, but it failed to account for changes in the economy.
Culture for Change: Implementing AI requires a cultural shift within banks, moving towards data-driven decision-making and continuous learning, which can be met with resistance from traditional banking professionals.
Employment Concerns: There is fear of job displacement due to AI automation. Banks must manage these concerns by reskilling employees for new roles in AI oversight and ethical AI usage. Emphasizing the symbiotic relationship between humans and AI can alleviate fears of job displacement. Demonstrating how AI can refine productivity, elevate the accuracy of decision-making procedures, and engender fresh vocational prospects in burgeoning AI-related sectors can help employees see the potential benefits of AI.
How can organizations build Generative AI use cases for their contextual needs?
Here are some steps that organizations can take to identify use cases for generative AI:
Bring together a cross-disciplinary team: Organizations should bring together a team of people with the domain knowledge to think creatively about potential use case. This team should include business leaders, domain experts, data scientists, and product managers.
Identify business problems: The team should identify business problems that can be solved using generative AI. For example, generative AI can be used to analyze sales data and customer interactions to identify patterns indicating the loss or risk of a potential sale.
Evaluate feasibility: The team should evaluate the feasibility of using generative AI to solve the identified business problems. They should consider factors such as the availability of data, the complexity of the problem, and the potential impact of the solution.
Prototype and test: Once the team has identified potential use cases and evaluated their feasibility, they should prototype and test the solutions. This will help them to refine the solutions and identify any issues that need to be addressed.
Ethical Considerations and Compliance: In the realm of generative AI, ethical use and compliance with regulatory standards are paramount. Organizations must navigate the moral implications of AI-generated content and ensure that their use cases respect privacy, security, and fairness.
Deploy and scale: Once the solutions have been refined and tested, they can be deployed and scaled across the organization. Organizations should monitor the performance of the solutions and make any necessary adjustments.
Continual Learning and Adaptation: The AI landscape is ever evolving, and organizations must stay abreast of technological advancements. Continual learning programs and workshops can keep teams informed and ready to adapt use cases as new AI capabilities emerge.
Representative case study on how organizations can drive ideation to launch of a particular challenge for ESG using Generative AI using Hackathon.
A large global bank recognizing the growing importance of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria, set out to integrate ESG factors more deeply into their investment strategies. The CIO, along with the ESG department, identified the potential for a generative AI to analyze vast datasets, generate ESG reports, and simulate the impact of ESG factors on investment portfolios.
Conceptualizing the Solution: The idea was to develop an AI that could not only analyze current ESG data but also predict future ESG trends and their financial implications. The AI would generate narrative reports for stakeholders and suggest portfolio adjustments to align with ESG goals.
Hackathon Planning: To kickstart innovation, the organization planned a hackathon, inviting AI experts, product developers, data scientists, and ESG analysts. The goal was to develop a prototype of the generative AI tool in a collaborative, competitive environment.
Hackathon Execution: During the hackathon, teams were provided with datasets, ESG scoring frameworks, and access to AI development tools. They were encouraged to create algorithms that could interpret complex data and generate predictive ESG models. Mentors from the business and technical domains provided guidance, ensuring alignment with business goals and technical feasibility.
Prototype Development: One team, leveraging natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning, developed a prototype that impressed the judges. The AI could not only analyze reports, news, and financial data but also generate comprehensive ESG impact reports that could inform investment decisions.
Post-Hackathon Development: Post-hackathon, a cross-functional team was formed to refine the prototype. They worked on improving the AI's accuracy, ensuring it could understand the nuances of ESG factors and their long-term implications on investments.
Integration and Testing: The AI was integrated into the bank’s existing investment analysis platform. Rigorous testing followed, including beta testing with a select group of clients who provided feedback on the usability and usefulness of the ESG reports generated by the AI.
Launching the AI Tool: With successful testing phases, the generative AI tool was officially launched. It was marketed as an innovative solution for investors looking to make more informed decisions based on ESG criteria. The tool could generate personalized investment reports, highlighting potential ESG risks and opportunities.
Continuous Improvement: The bank established a cycle of continuous feedback and improvement, using insights from user interactions to enhance the AI's capabilities. The generative AI tool became a unique selling proposition for the bank, attracting clients interested in sustainable investing and showcasing the bank's commitment to innovation and ESG principles.
How can 3rd party system integrator firms help?
Large system integrators with domain and technology expertise can play a crucial role in training and tuning models to support generative AI by providing a range of services.
When engaging third-party vendors for training and tuning models to support generative AI, it's essential to enforce key guard rails to ensure that the project is successful, secure, and ethical. Here are some guard rails to consider:
Confidentiality Agreements: Ensure that all sensitive data and intellectual property are protected by strict non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) with the SI.
Privacy by Design: Incorporate privacy at the initial design phase of AI modeling. This involves using anonymization techniques, like differential privacy, to ensure that the training data cannot be traced back to individuals. Ensure that the vendor has robust data privacy and security measures in place to protect sensitive data. This includes data encryption, access controls, and data anonymization.
Secure Data Environments: Utilize encrypted environments and secure data storage solutions to protect training datasets and AI models from unauthorized access and potential breaches. SI resources should develop within the approved network perimeter.
Regulatory Compliance: Stay abreast of and comply with global data protection regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA, which dictate how personal data should be handled and processed.
Access Control: Implement stringent access controls so only authorized personnel can handle sensitive data. Role-based access ensures that each team member can only access the data necessary for their work
Model Performance and Accuracy: Set clear expectations for model performance and accuracy. Establish metrics to measure model performance and ensure that the vendor is held accountable for meeting those metrics.
Model Explainability: Ensure that the vendor provides model explainability techniques to understand how the generative model works and makes decisions. This includes providing feature importance, partial dependence plots, and SHAP values.
Model Bias and Fairness: Ensure that the vendor takes steps to mitigate model bias and ensure fairness. This includes using diverse and representative data, using fairness-aware algorithms, and testing the model for bias.
Intellectual Property: Establish clear ownership and licensing agreements for the trained models. Ensure that the vendor does not retain any rights to the models or data without your explicit consent.
Vendor Lock-in: Avoid vendor lock-in by ensuring that the models are deployable across multiple platforms and environments. This includes using open-source technologies and avoiding proprietary formats.
Project Management: Establish clear project management processes, including timelines, milestones, and deliverables. Ensure that the vendor provides regular updates and progress reports.
Technical Support: Ensure that the vendor provides ongoing technical support for the trained models, including bug fixes, security patches, and updates.
Compliance and Regulation: Ensure that the vendor complies with relevant regulations, such as GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA, and industry standards, such as PCI-DSS and ISO 27001.
Continuous Improvement: Establish a culture of continuous improvement, encouraging the vendor to innovate and improve the models over time. This includes providing feedback mechanisms and incentives for improvement.
In conclusion, embracing GenerativeAI is an imperative step for enterprises seeking to solidify their leadership and innovate proactively in a rapidly evolving digital landscape. The strategic integration of AI into various facets of an organization, underscored by robust infrastructure, visionary leadership, and a culture of continuous innovation, will propel businesses towards unprecedented operational excellence and competitive differentiation. By harnessing the transformative power of AI, companies can unlock new efficiencies, foster groundbreaking product development, and deliver enhanced customer experiences. The journey of AI integration, therefore, is not just a technological upgrade but a fundamental renaissance of business models and strategies.